Why do we need to eat fat and which ones are ‘good’ for us?
If you are very new to nutrition you may wish to read ‘An introduction to nutrition first‘
Why do we need fat?
Fat is a major source of energy (9Kcals per g), it helps the body absorb vitamins and helps food taste good.
But what else does it do? You don’t have to understand what all of this means, all you need to understand is that good fat is incredibly important for us.
Some other functions include:
- Formation of cell membranes
- Formation of myelin sheath within the nervous system
- Constitute a large majority of the central nervous system and the spinal cord
- Synthesis of steroid hormones
- Assist in the regulation of enzymes
- Protection of internal organs
- Allowing absorption of Vitamins A, D, E and K into the body
- Essential for good brain function
- and more!
At present dietary recommendations for fats are under debate but the roles played by fats within the body cannot be underestimated.
The science bit
Fat structure
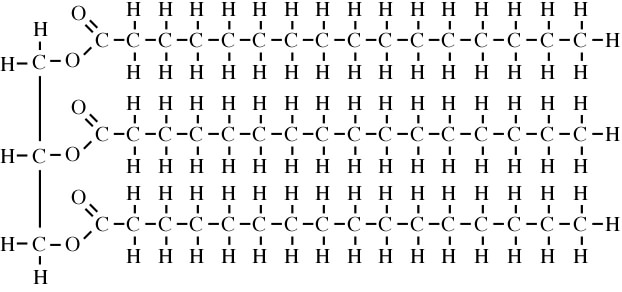
Fat consists of chains or rings of carbon atoms joined together by other atoms, most commonly hydrogen and oxygen. There are many types of fat and they vary due to their structure.
(Triglycerides)
Fatty acids
- Fatty acids are the acids that are produced when fats are broken down
- They are considered to be good fats
- They naturally occur as triglycerides, where 3 fatty acids attached to a carbohydrate backbone called glycerol, during digestion the fatty acids are broken off and used in the body as required
Benefits of Triglycerides
- Fatty acids help keep skin healthy
- Prevent early aging
- Help the body process cholesterol
- Help get rid of cholesterol build-up
- And assist the adrenal and thyroid gland
- All of which in turn would assist in regulating weight
Saturated fat
In saturated fats, the chains are saturated with hydrogen. Saturated fats are straight and tend to arrange themselves uniformly, which is why they tend to be solid at room temperature. They also tend to be more chemically stable and less likely to ‘change’ when heated or exposed to oxygen.
Saturated Fat:
Animal
- Meat (beef, pork, lamb, venison)
- Poultry (chicken, duck, goose)
- Dairy (milk, cheese, yogurt, cream, butter, eggs)
Non – Animal
- Coconut oil
- Palm oil
- Cocoa butter
Unsaturated fats
The hydrogen atoms are missing from portions of the chains and there is often bending or kinking in the chain. This leads to a less uniform and more fluid arrangement and is typically liquid at room temperature (oils). These are more unstable and reactive. They come in two main categories Monounsaturated and Polyunsaturated.
Monounsaturated
Monounsaturated fats contain fatty acids with only one double bond. The body is able to recognise the shape of various monounsaturated fatty acids and utilise them accordingly. They lower LDL (low-density lipoproteins), cholesterol, and plasma triglycerides (fat in the blood) and therefore reduces the risk of Heart disease.
Monounsaturated:
- Olives / Olive Oil
- Avocado
- Lard
- Beef dripping
- Rapeseed oil
- Peanut oil
- Nuts
- Seeds
Polyunsaturated
Polyunsaturated fats are missing hydrogen in more than one area so have more than one double bond. The positioning of the double bond defines the type of Polyunsaturated Fat. Two are considered essential to health and are commonly known as essential fatty acids. The body is not able to Synthesise these itself.
- OMEGA 3 FATTY ACIDS
- OMEGA 6 FATTY ACIDS
Essential fatty acids
Essential fatty acids play a fundamental role in numerous metabolic processes and are very specific to the functioning of the cell. They must be eaten in the required amounts to promote good health. Omega 3 fatty acids found in oily fish are particularly beneficial.
OMEGA 3
- Oily Fish
- Cod Liver Oil
- Flax oil
- Walnut Oil
- Hemp Seeds oil
- Pasture-rearer Eggs
OMEGA 6
In the western diet Omega 6 is highly overused which can be a problem as can:
- Stimulate inflammatory pathways in the body
- Promote the formation of blood clots
- Promote an increase in cellular growth, leading to cancer
- Leads to arthritis, mood disorders, Osteoporosis, and obesity
Fats and Disease
There is a significant link between disease and the increasing consumption of processed fats. A common process is Hydrogenation, where cheap vegetable oils are converted into solid spreadable fats through a process of heating and chemical manipulation. A by-product of this process is Trans fat.
Trans fat
Trans fat increases bad cholesterol and is associated with cancer, diseased arteries, diabetes, obesity, immune system dysfunction and problems with bones and tendons.
Products including Transfats include:
- Margarine
- biscuits
- crackers
- cakes
- take away
- pies
- pastry
- ready meals
- processed food
Summary
Nothing needs to be completely off bounds but we should be mindful of the quantities in which we eat.
Monounsaturated – good:
- Olives / Olive Oil
- Avocado
- Peanut oil
- Nuts
- Seeds
Polyunsaturated
OMEGA 3 – good and essential as there is not enough in our diet:
- Oily Fish
- Canola oil
- Cod liver oil
- Flaxseed oil
- Mustard oil
- Soybean oil
- Walnut oil
Remember these do not like to be heated as it destroys the molecular structure.
OMEGA 6 – overused in the west so be mindful:
- Certain vegetable oils
- Salad dressings & mayonnaise
- Snacks made with Omega-6 Rich fats
- Fast foods made with Omega-6 Rich Fats
- Cookies, candies, cakes, pastries & muffins
- Pork products
- Chicken
- Dairy & Egg
- Beef
Saturated fat – a little is OK:
- Animal fat
- Cream
- Cheese
- Butter
- Coconut Oil
Trans fat – be very mindful:
- Processed foods
- Margarine
- Shortening
Fats are a little complicated but remember they are essential so do not leave them out.
‘Good’ fats (HDL) will also help to get rid of ‘bad’ fats (LDL) so they are all the more important if you are trying to reduce cholesterol build-up.






Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!